Introduction
A key ingredient in the Mediterranean diet is olive oil. Antioxidants are abundant in it. Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), that are regarded by experts as a healthy fat, make up the majority of the fat in it. Olive oil’s antioxidants may aid in shielding the body against cellular damage, which can result in a variety of illnesses and ailments. Extra virgin oil includes a bitter taste, but because it is processed the least, it possesses greater levels of antioxidants than other varieties.
Olive oil, however, is distinct, particularly when combined with other healthful, least processed or unprocessed meals. Every oil is not made equally. Extra virgin, virgin, and refined olive oils are the three types. There are no chemicals or heat-related changes made to extra virgin oil. It is the most similar process to pressing fresh oil.
Nutrition
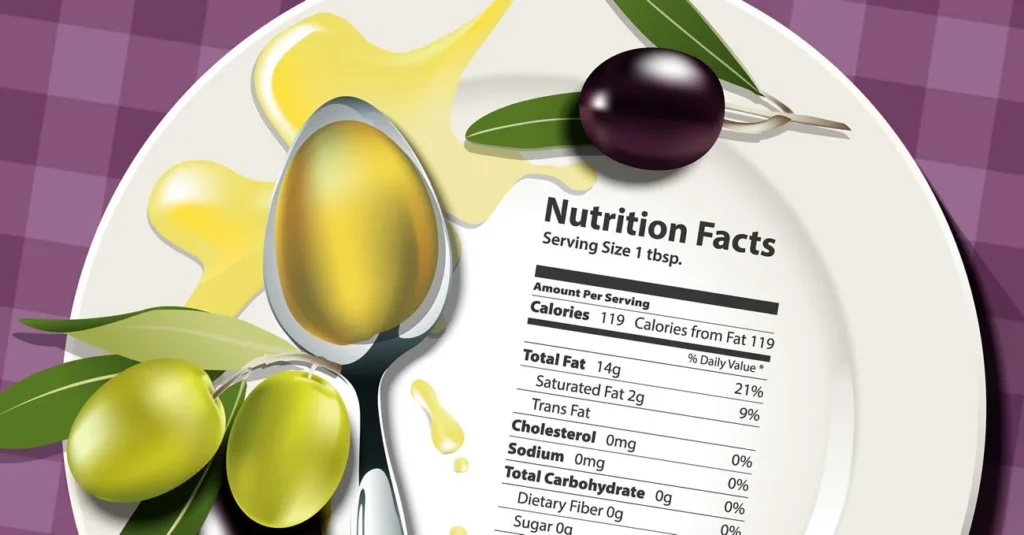
- One tablespoon, or 13.5 grams (g), of oil offers 119 calories, based on the United States Ministry of Agricultural (USDA).
- A dosage of 1.9 mg of vitamin E
- 8.13 vitamin K micrograms (mcg)
- 13.5 grams of fat, 1.86 grams of which are saturated
Together with tocopherols, polyphenols, phytosterols, squalene, terpenic acids, and other antioxidants, it also has trace amounts of calcium and potassium.
Health Benefits
The health advantages of this oil have been the subject of numerous studies. The highest quality oil on the market, extra virgin oil, is full of antioxidants that guard against the harm that free radicals, a type of molecule cause to cells. The body creates free radicals as a byproduct of metabolism and other bodily functions. Free radicals are neutralized by antioxidants.
Oxidative stress may result from an accumulation of free radicals that is excessive. This may result in cell damage and contribute to the emergence of specific illnesses, such as some forms of cancer.
High in Antioxidant
Antioxidants found in extra virgin oil, such as tocopherols, phytosterols, Polyphenols, terpenes, squalene and vitamin E, help shield cells from harm caused by free radicals. Oxidative stress brought on by an excess of free radicals can harm cells. It might contribute to the emergence of specific illnesses, such as some forms of cancer.
Learn More About Antioxidant Properties.
Anti-Inflammatory Characteristics
Numerous diseases, including cancer, type 2 diabetes, dementia, arthritis, obesity, heart issues, and others, are mostly brought on by chronic inflammation. Polyphenols, a naturally occurring substance with strong anti-inflammatory qualities found in olive oil, can help relieve inflammation. A study found that anti-inflammatory qualities, such as those found in the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen, can aid in the reduction of inflammation.
Beneficial to Heart Health
The main fat resource in the diet known as the Mediterranean diet is this oil, which is linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and a higher life expectancy than other diets. This oil lowers inflammation, raises cholesterol, and keeps blood vessels in good condition, all of which are beneficial to cardiovascular health. To keep your heart healthy, try consuming 20 grams, or two teaspoons, of extra virgin oil every day.

Beneficial Monosaturated Fats
10.5% of this oil is made up of polyunsaturated fatty acids like omega-3 and omega-6, whereas 13.8 percent of the oil it contains is saturated fat. However, oleic acid, a type of monounsaturated fat that accounts for 71% of the oil content overall, is the main fatty acid found in this oil. Oleic acid lowers oxidative stress and inflammation and could have positive effects on cancer-related genes. Extra virgin oil from olives is a good choice for cooking due to monounsaturated fats can tolerate high temperatures effectively.
Anti-Bacterial Qualities of Olive Oil
Compounds in oil of olive have the potential to suppress or eradicate dangerous germs. Helicobacter pylori, often known as H. pylori, is a type of bacteria that resides in the stomach and has the potential to cause both stomach cancer and ulcers. Extra virgin oil could help in the defense against specific strains of this bacterium, according to a 2022 animal study. Nevertheless, additional human study is required to validate oil’ antimicrobial properties. Other, more well researched methods exist for treating H. pylori.
Enhances Digestion
Including olive oil in your diet on a regular basis can aid in digestion. Studies reveal that the gut can absorb polyphenols from olive oil directly. These polyphenols may help keep the gut microbiota in a healthy state, which is linked to less inflammation and enhanced immunity. A single tablespoon of natural olive oil taken in the morning will help relieve constipation in a lot of healthy persons.
Cancer Fighting Qualities
The World Health Organization (WHO) lists cancer as one of the top causes of mortality globally. Olive oil contains anti-inflammatory and antioxidant chemicals that help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, two factors that lead to the development of cancer. According to a 2022 meta-analysis released by Science One and the Public Library, individuals who ate olive oil had a 31% lower risk of developing cancer.
Avoid Weight Gain And Obesity
Overindulging in calories can result in gaining weight, and fats contain many calories. Nonetheless, a number of studies have connected the olive oil-rich Mediterranean diet to positive benefits on body weight. Additionally, 2018 research discovered that diets rich in oil were more effective in promoting weight loss than meals deficient in this oil. But it’s crucial to remember that eating too much of anything, including olive oil, might make you gain weight.
Side Effects of Olive Oil
When Ingested Orally
Olive oil is frequently found in meals. For as long as 5.8 years, using a maximum of one Liter of extra virgin olive oil per week as a component of a Mediterranean-style diet has proved safe. In most cases, olive oil is well tolerated. There is a chance that it will make some people sick.
When Use Olive Oil on Skin
There have been reports of delayed allergic responses. Your mouth can become more sensitive after receiving dental treatment when using this.
Precautions
Olive Oil And Diabetes
It may reduce blood sugar. When consuming olive oil, diabetics should monitor their blood sugar levels.

Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
The safety of consuming olive products while pregnant or nursing is not well enough documented. Never use more than what is typically present in food items.
Surgery
Olive oil may impact blood sugar during surgery. Olive oil use may have an impact on blood sugar regulation both before and after surgery. Give up olive oil two weeks before to surgery.
Dosage of Olive Oil
Several dosages have been examined in research studies. By mouth:
Constipation
30 milliliters of olive oil can help with constipation.
For High Cholesterol
To lower cholesterol, replace the saturated fats in your diet with 17 g of mono unsaturated fats by consuming 23 grams of olive oil daily, or roughly 2 tablespoons.
For High Blood Pressure
Include 30–40 grams of pure olive oil in your diet each day to help lower high blood pressure. For high blood pressure, 400 mg of extract from olive leaves four times a day has also been utilized.

For Preventing Heart Disease
It has been used to prevent heart attacks and heart disease by taking 54 grams (approximately 4 tablespoons) every day. Up to one liter of extra-virgin oils from olives weekly has also been used as a component of a Mediterranean diet.


casino online 24bet-casino.com .