Introduction
Red blood cells carry hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein that attaches to the oxygen in the lungs and carries it to tissues of the body. Anemia occurs when red blood cells are not sufficient in number or when red blood cells do not function properly. Anemia is diagnosed when a blood test of a person shows the hemoglobin value of less than 13.5 gm/dl in a man or less than 12.0 gm/dl in a woman. Normal values in children vary with age.
Sign And Symptoms
- shortness of breath
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Tachycardia
- Tinnitus
- Headache
- Cold hands or feet
- Pale or yellow skin
- Chest pain
Risk Factors
- Old Age
- Poor diet
- Intestinal disorders (Inflammatory bowel disease i.e. Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis)
- Chronic medical diseases (Rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune disease, Kidney disease, Cancer, Liver disease, Thyroid disease etc.)
- Infections
- Women who are menstruating or pregnant are most at risk for this disease
Common Types of Anemia
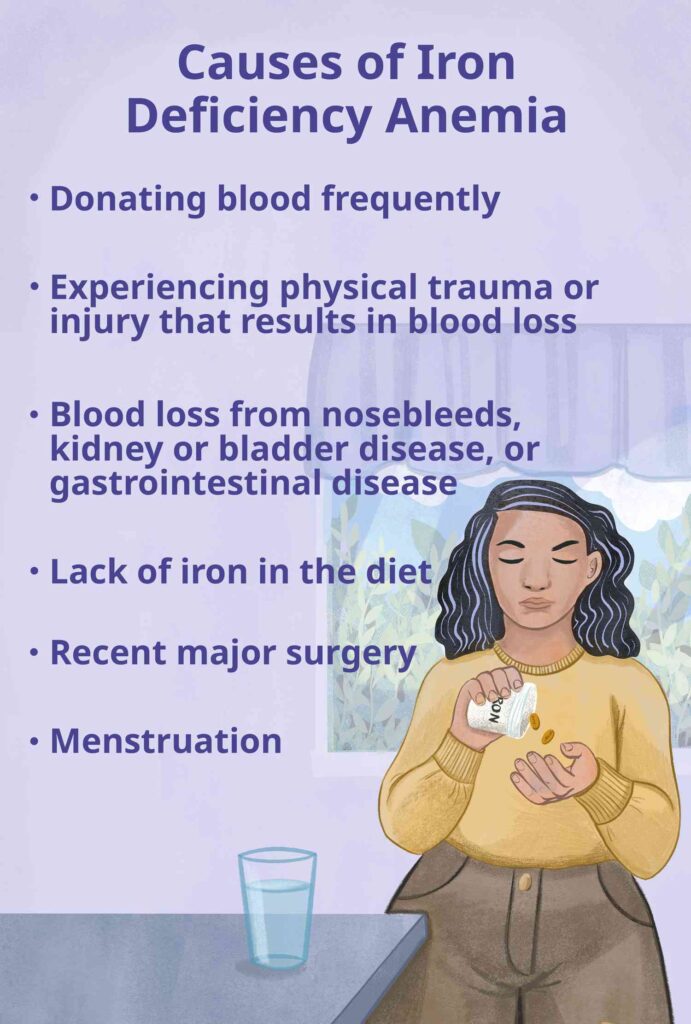
Iron-Deficiency Anemia
It is the most common type of this disease. It happens due to the iron deficiency in the body. This is usually due to blood loss or may occasionally be due to poor absorption of iron. Pregnancy and childbirth consume a lots of iron and thus can results in pregnancy-related anemia. People who have had gastric bypass surgery for loss of weight or other reasons may also be iron deficient due to poor absorption.
Vitamin-Deficiency Anemia
Vitamin deficiency anemia may result from low levels of folate (folic acid) and vitamin B12. It is usually due to poor diet intake. Pernicious anemia is a condition in which vitamin B12 in not absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
Aplastic Anemia
This is a rare bone marrow failure disorder in which the bone marrow stops making enough red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This occurs as a result of destruction or deficiency of blood-forming stem cells in the bone marrow, in particular when the body’s own immune system attacks the stem cells. However, the bone marrow does make few blood cells which are normal. Ionizing radiation, viral infections, and exposure to toxic chemicals or drugs can also the causes of aplastic blood anemia.
Hemolytic Anemia
It occurs when red blood cells are broken up in the bloodstream or in the spleen. Haemolytic may be due to mechanical causes such as leaky heart valves or aneurysms. It is also due to infections, autoimmune disorders, or congenital abnormalities in the red blood cell. Examples of inherited hemolytic anemia include some types of thalassemia and reduced levels of enzymes such as glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase.
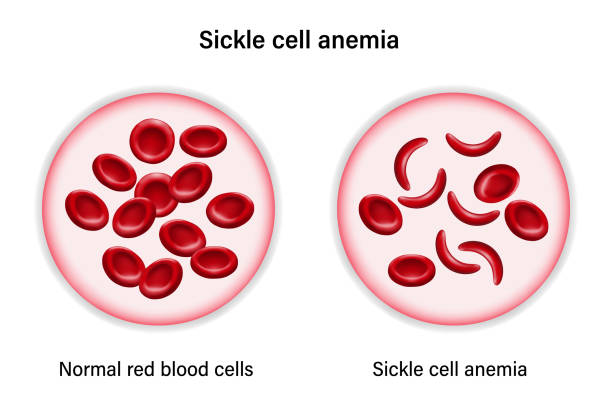
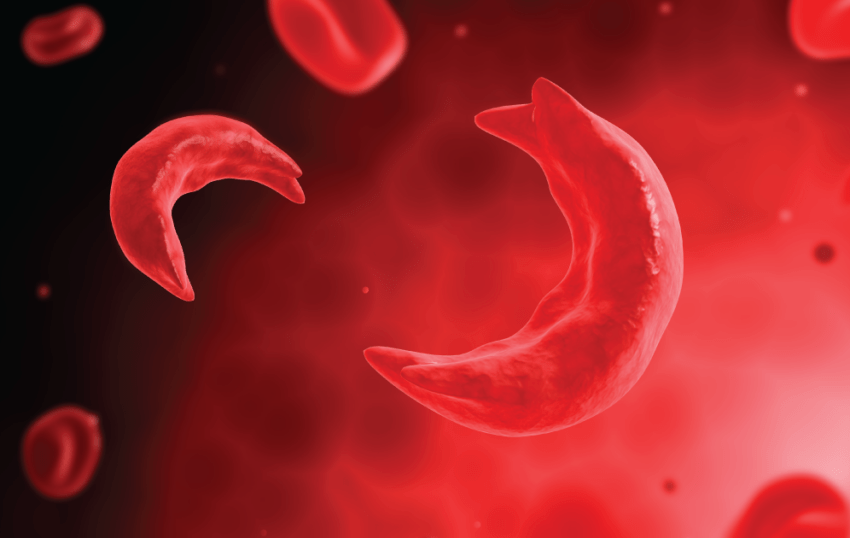
Sickle Cell Anemia
It is an inherited haemolytic anemia. In which the hemoglobin protein is abnormal. Cells become sickled shape. It causing the red blood cells to be rigid and clog the circulation. Because these RBC’s are unable to flow through small blood vessels.
Anemia Caused By Other Diseases
Some diseases can affect the body’s ability to make red blood cells. For example, some patients with kidney disease develop this disease. Because the kidneys are making low level of hormone erythropoietin. Erythropoietin gives signal the bone marrow to make new or more red blood cells. Chemotherapy is a treatment which is used to treat various cancers which often impairs the body’s ability to make new red blood cells and anemia often results from this treatment.
Treatment
The cause will determine how you are treated. Your healthcare practitioner will address any underlying conditions if your anemia is a result of them. However, they might also administer the following anemia-specific therapies. Medication or dietary supplements may be used as treatments.
Nutritional Supplements
For anemia, your doctor could suggest the following supplements:
Supplements Containing Iron
You can take this supplement orally via a glass of water in the form of capsules or tablets.
Supplements Containing Folic Acid
Folate, often known as vitamin B9, is a necessary vitamin that aids in the formation of red blood cells with DNA, the fundamental building blocks of the human body.
Supplements containing vitamin B12
Supplements containing vitamin B12 help to produce red blood cells that are healthy.
Medications
Physicians may recommend the following drugs to treat anemia:
Erythropoietin
This drug stimulates the production of red blood cells in your bone marrow.
Immunosuppressants
Your doctor may recommend medication to prevent the immune system from destroying the red blood cells in your body if you have this due to an autoimmune illness.
Procedures
In certain circumstances, your supplier might advise:
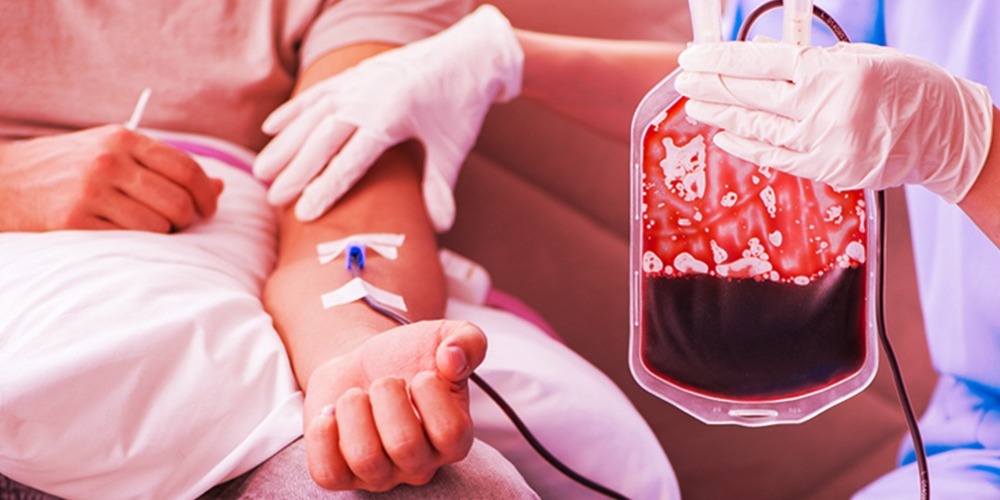
- Red blood cell replacement with blood transfusion
- This causing internal bleeding is treated surgically
- Bone marrow stem cell transplant to substitute good blood stem cells for diseased ones
Can I treat my own anemia?
When blood deficiency is determined to be the source of certain symptoms by a healthcare expert, you may be able to treat the condition temporarily by making dietary changes or taking supplements. Anemia typically results in minor symptoms. However, other diseases’ symptoms can be brought on by anemia. For instance, you might not be anemic if you feel worn out regardless of how much sleep you get. If you have weariness or other alterations in the way you feel that do not go away after two weeks, consult your healthcare professional. After determining the cause of your symptoms, they will treat the illness.
Prevention
Iron-deficiency is the most prevalent kind, but it may be avoided if you incorporate foods high in iron into your regular meals and snacks. However, some forms of this disease, such as those caused by genetic diseases, are unavoidable.

I always feel more informed after reading your posts. Thanks for sharing!